anyspace
React常见问题
2022年7月29日 • ☕️ 6 min read阅读量 : •••


setState是同步还是异步的
举个🌰
// legacy模式下
class App extends React.Component {
state = { val: 0 }
componentDidMount() {
this.setState({ val: this.state.val + 1 })
console.log(this.state.val)
this.setState({ val: this.state.val + 1 })
console.log(this.state.val)
setTimeout(_ => {
this.setState({ val: this.state.val + 1 })
console.log(this.state.val);
this.setState({ val: this.state.val + 1 })
console.log(this.state.val)
}, 0)
}
render() {
return <div>{this.state.val}</div>
}
}结果: 钩子函数中的 setState 无法立马拿到更新后的值,所以前两次都是输出0,当执行到 setTimeout 里的时候,前面两个state的值已经被更新,由于 setState 批量更新的策略, this.state.val 只对最后一次的生效,为1,而在 setTimeout 中 setState 是可以同步拿到更新结果,所以 setTimeout 中的两次输出2,3,最终结果就为 0, 0, 2, 3 。
结论
合成事件:即
react为了解决跨平台,兼容性问题,自己封装了一套事件机制,代理了原生的事件,像在jsx中常见的onClick、onChange这些都是合成事件。
legacy模式下
setState只在合成事件和钩子函数中是“异步”的,在原生事件和setTimeout中都是同步的。setState的“异步”并不是说内部由异步代码实现,其实本身执行的过程和代码都是同步的,只是合成事件和钩子函数的调用顺序在更新之前,导致在合成事件和钩子函数中没法立马拿到更新后的值,形式了所谓的“异步”,当然可以通过第二个参数setState(partialState, callback)中的callback拿到更新后的结果。setState的批量更新优化也是建立在“异步”(合成事件、钩子函数)之上的,在原生事件和setTimeout中不会批量更新,在“异步”中如果对同一个值进行多次setState,setState的批量更新策略会对其进行覆盖,取最后一次的执行,如果是同时setState多个不同的值,在更新时会对其进行合并批量更新。
concurrent模式下
- 都表现为‘异步’
原理
不仅仅是setState了, 在对 function 类型组件中的 hook 进行操作时也是一样, 最终决定setState是同步渲染还是异步渲染的关键因素是ReactFiberWorkLoop工作空间的执行上下文.
详细代码点击查看
export function scheduleUpdateOnFiber(
fiber: Fiber,
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
) {
const priorityLevel = getCurrentPriorityLevel();
if (expirationTime === Sync) {
if (
// Check if we're inside unbatchedUpdates
(executionContext & LegacyUnbatchedContext) !== NoContext &&
// Check if we're not already rendering
(executionContext & (RenderContext | CommitContext)) === NoContext
) {
performSyncWorkOnRoot(root);
} else {
ensureRootIsScheduled(root);
schedulePendingInteractions(root, expirationTime);
if (executionContext === NoContext) {
// Flush the synchronous work now, unless we're already working or inside
// a batch. This is intentionally inside scheduleUpdateOnFiber instead of
// scheduleCallbackForFiber to preserve the ability to schedule a callback
// without immediately flushing it. We only do this for user-initiated
// updates, to preserve historical behavior of legacy mode.
flushSyncCallbackQueue();
}
}
} else {
// Schedule a discrete update but only if it's not Sync.
if (
(executionContext & DiscreteEventContext) !== NoContext &&
// Only updates at user-blocking priority or greater are considered
// discrete, even inside a discrete event.
(priorityLevel === UserBlockingPriority ||
priorityLevel === ImmediatePriority)
) {
// This is the result of a discrete event. Track the lowest priority
// discrete update per root so we can flush them early, if needed.
if (rootsWithPendingDiscreteUpdates === null) {
rootsWithPendingDiscreteUpdates = new Map([[root, expirationTime]]);
} else {
const lastDiscreteTime = rootsWithPendingDiscreteUpdates.get(root);
if (
lastDiscreteTime === undefined ||
lastDiscreteTime > expirationTime
) {
rootsWithPendingDiscreteUpdates.set(root, expirationTime);
}
}
}
// Schedule other updates after in case the callback is sync.
ensureRootIsScheduled(root);
schedulePendingInteractions(root, expirationTime);
}
}可以看到, 是否同步渲染调度决定代码是flushSyncCallbackQueue(). 进入该分支的条件:
- 必须是legacy模式, concurrent模式下expirationTime不会为Sync
- executionContext === NoContext, 执行上下文必须要为空.
两个条件缺一不可。
Fiber
什么是Fiber
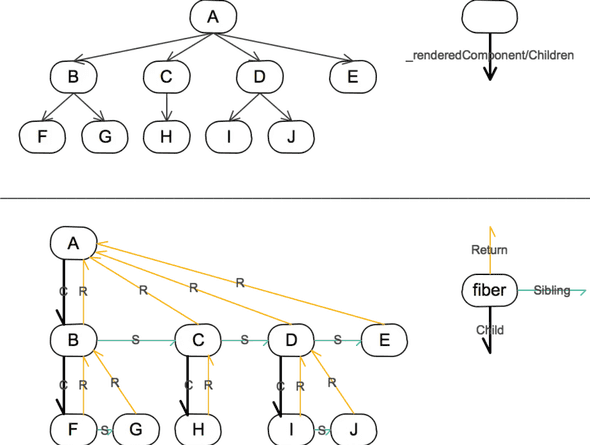
其实是一种数据结构:
const fiber = {
stateNode, // 节点实例
child, // 子节点
sibling, // 兄弟节点
return, // 父节点
}为什么引入Fiber
React可以分为3层:
Virtual DOM层,描述页面长什么样。Reconciler层,负责调用组件生命周期方法,进行Diff运算等。Renderer层,根据不同的平台,渲染出相应的页面,比较常见的是ReactDOM和ReactNative。
Fiber引入后,Reconciler有了新名字Fiber Reconciler。
以前的Stack Reconciler运行过程不可打断。
而Fiber Reconciler 每执行有单时间,都可以将控制权交回浏览器,可以分段执行。
为了达到可中断的效果,就需要一个调度器Scheduler来进行任务分配。优先级有以下几种:
- synchronous,与之前的Stack Reconciler操作一样,同步执行
- task,在next tick之前执行
- animation,下一帧之前执行
- high,在不久的将来立即执行
- low,稍微延迟执行也没关系
- offscreen,下一次render时或scroll时才执行
优先级高的任务(如键盘输入)可以打断优先级低的任务(如Diff)的执行,从而更快的生效。
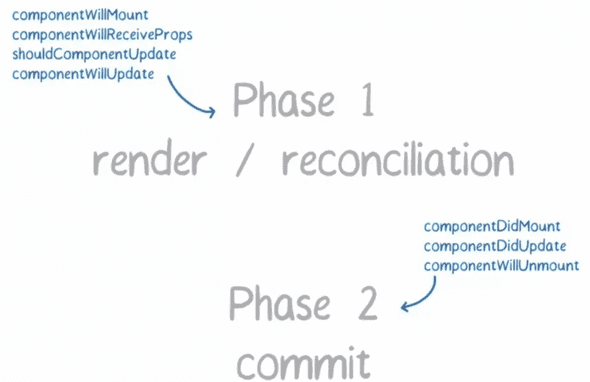
Fiber Reconciler在执行中分为两个阶段:
- 阶段一,生成 Fiber 树,得出需要更新的节点信息。这一步是一个渐进的过程,可以被打断。
- 阶段二,将需要更新的节点一次过批量更新,这个过程不能被打断。
Fiber树
Fiber Reconciler 在阶段一进行 Diff 计算的时候,会生成一棵 Fiber 树。这棵树是在 Virtual DOM 树的基础上增加额外的信息来生成的,它本质来说是一个链表。
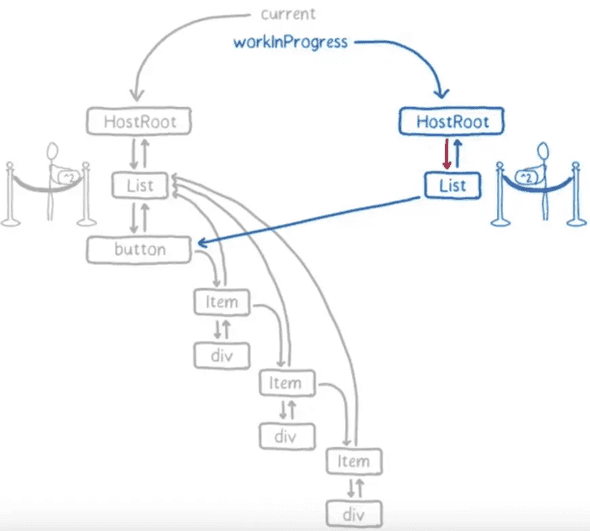
Fiber 树在首次渲染的时候会一次过生成。在后续需要 Diff 的时候,会根据已有树和最新 Virtual DOM 的信息,生成一棵新的树。这颗新树每生成一个新的节点,都会将控制权交回给主线程,去检查有没有优先级更高的任务需要执行。如果没有,则继续构建树的过程:
如果过程中有优先级更高的任务需要进行,则 Fiber Reconciler 会丢弃正在生成的树,在空闲的时候再重新执行一遍。
在构造 Fiber 树的过程中,Fiber Reconciler 会将需要更新的节点信息保存在Effect List当中,在阶段二执行的时候,会批量更新相应的节点。

一个记录知识和生活的神秘小空间